Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
1.5.12.16. Optimization of a two-parameter function¶
import numpy as np
# Define the function that we are interested in
def sixhump(x):
return ((4 - 2.1*x[0]**2 + x[0]**4 / 3) * x[0]**2
+ x[0] * x[1] + (-4 + 4*x[1]**2) * x[1]**2)
# Make a grid to evaluate the function (for plotting)
xlim = [-2, 2]
ylim = [-1, 1]
x = np.linspace(*xlim)
y = np.linspace(*ylim)
xg, yg = np.meshgrid(x, y)
A 2D image plot of the function¶
Simple visualization in 2D
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.figure()
plt.imshow(sixhump([xg, yg]),
extent=xlim+ylim,
origin="lower")
plt.colorbar()
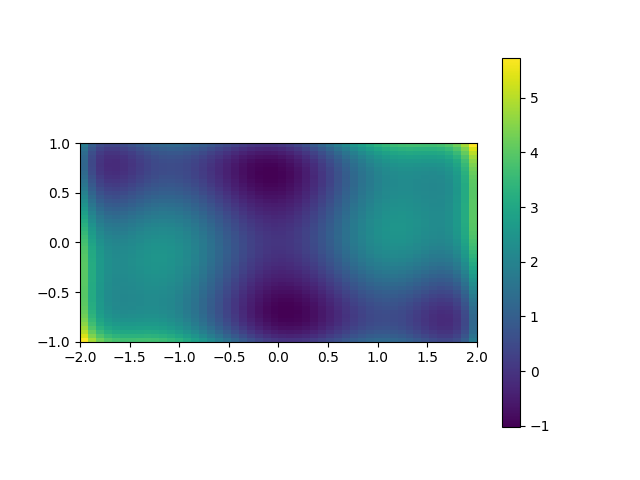
<matplotlib.colorbar.Colorbar object at 0x7fe7b05db310>
A 3D surface plot of the function¶
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
surf = ax.plot_surface(xg, yg, sixhump([xg, yg]), rstride=1, cstride=1,
cmap=plt.cm.viridis, linewidth=0, antialiased=False)
ax.set_xlabel('x')
ax.set_ylabel('y')
ax.set_zlabel('f(x, y)')
ax.set_title('Six-hump Camelback function')
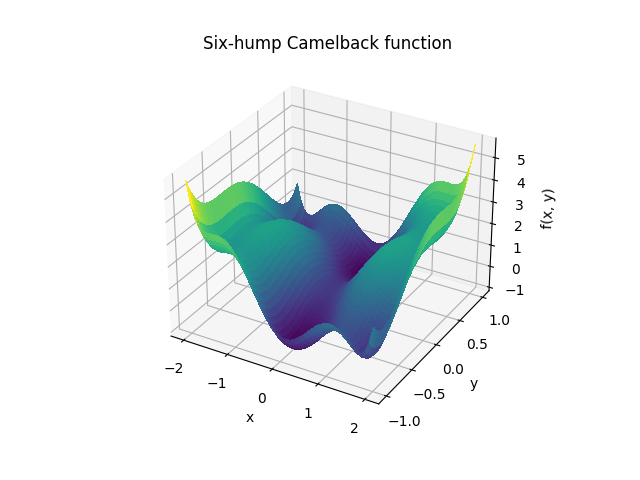
Text(0.5, 1.0, 'Six-hump Camelback function')
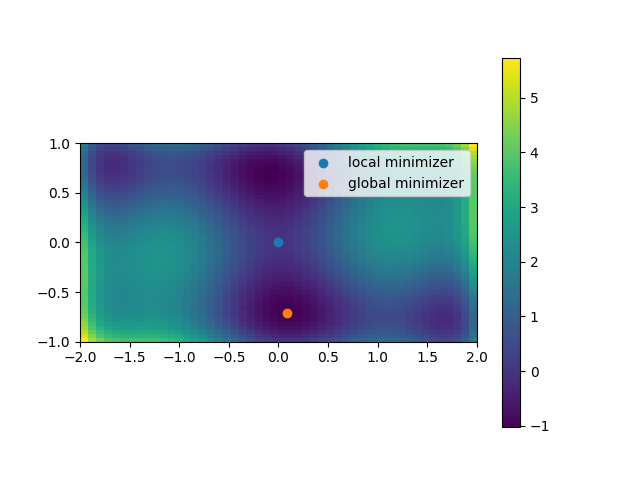
Find minima¶
import scipy as sp
# local minimization
res_local = sp.optimize.minimize(sixhump, x0=[0, 0])
# global minimization
res_global = sp.optimize.differential_evolution(
sixhump, bounds=[xlim, ylim])
plt.figure()
# Show the function in 2D
plt.imshow(sixhump([xg, yg]),
extent=xlim+ylim,
origin="lower")
plt.colorbar()
# Mark the minima
plt.scatter(res_local.x[0], res_local.x[1], label='local minimizer')
plt.scatter(res_global.x[0], res_global.x[1], label='global minimizer')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 0.288 seconds)
